DRC for example, a central African country that has hardly known peace since independence, and where rape and sexual violence are commonly used as weapons of war, has over 5 million internally displaced people and 15.6 million people in need of humanitarian assistance and protection. Hampering humanitarian access is devastating in such a context, but closed international borders are today severely limiting the amount of life saving medical supplies and personal protective equipment that are so sorely needed, particularly as the country now, tragically, has seen new cases of Ebola in recent weeks.
In Iraq too, where more than 1.4 million people remain displaced, most of them as a result of the conflict with armed groups, and the military operations that ended in 2017; blockades and road closures leave a large number of day laborers living in displacement camps without jobs and income because they cannot commute to their places of work.
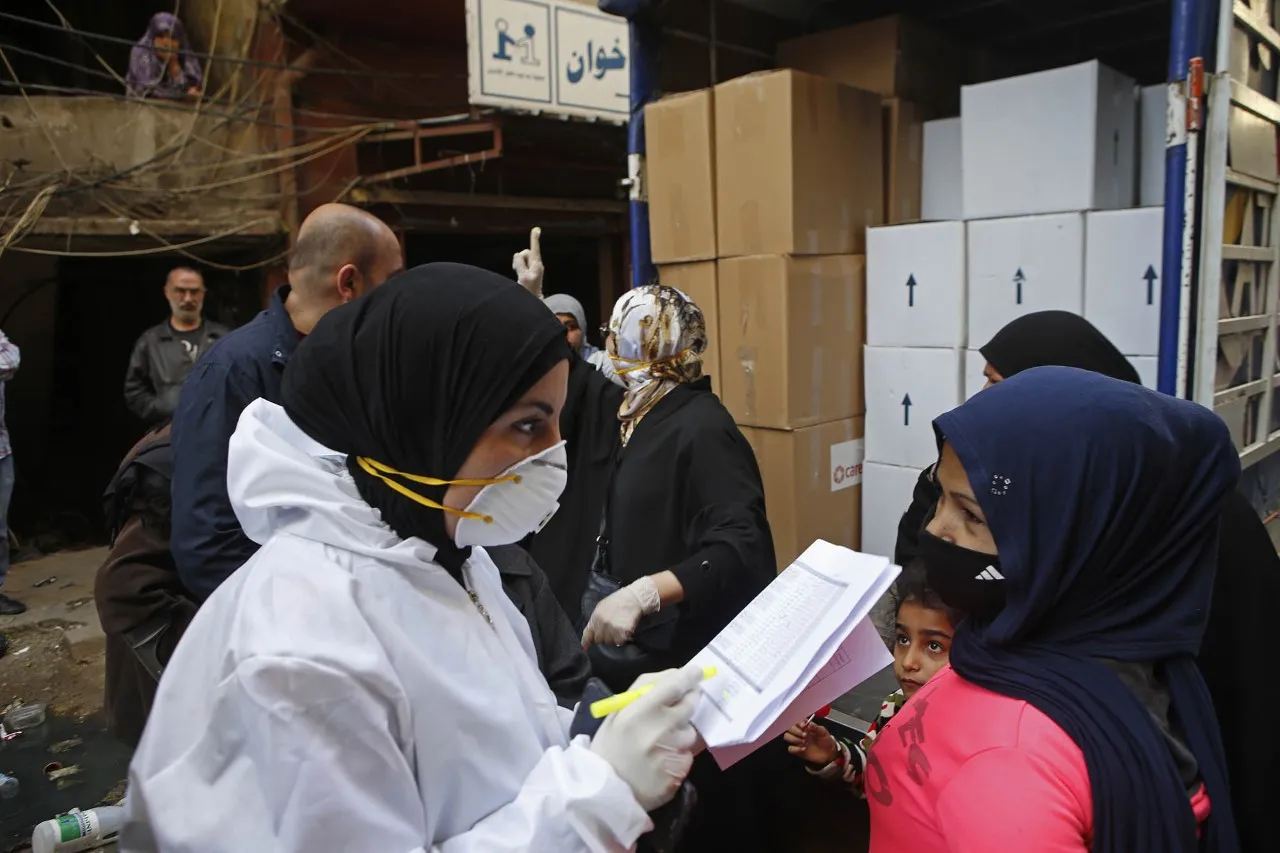
These examples mirror many more the world over. Humanitarian organizations are struggling to secure movement permits for their staff who deliver lifesaving assistance, or for the essential supplies they need to do their work. This urgently needs to change.
Despite this, aid organizations like CARE are used to working “business unusual,” and our staff and partners on the ground are rising to the unique challenges faced by COVID-19 with hope, courage and creativity; working around the clock and using innovative adjustments to our programs to ensure that the most vulnerable individuals can access life-saving support while doing all they can to respect and promote social distancing measures in sometimes very overcrowded and difficult places..
In Haiti, for example, spreading awareness about COVID-19 is done using radio and mobile campaigns; using boom box sound systems to spread messages from cars or bicycles. In Turkey and Jordan, hotlines, helpdesks and social media help us to collect feedback, disseminate health advice, and prioritise which areas need more supplies or support.
The dimensions of the pandemic that affect women and girls is also front of mind for humanitarian organisations such as CARE, and the increase in domestic violence as a result of lock downs and restrictions is a horrendous but increasingly pervasive dimension of this pandemic. Our partners and staff are adopting digital platforms to find ways to support women at risk, for example in Ecuador by using emoji codes to help women in quarantine safely report and ask for help.
And while we know that this pandemic creates a perfect storm of risk factors for women globally, we also know from our experience of handling previous epidemics such as Ebola and Zika, that women – given their front-line interaction as healthcare and social workers, and their participation in much of the care work – are incredibly well placed to influence and help design prevention activities and community engagement.
That’s why in the Philippines, for example, we are supporting local women leaders to keep markets functioning by safely delivering fresh vegetables from farms to families in crisis, while in Niger, we are working with our partners to find digital solution to enable women in our village savings and loans schemes to access more business capital.
As COVID-19 continues to challenge the humanitarian community to pivot and innovate at speed, the humanitarian imperative of this pandemic needs more priority – particularly in terms of ensuring that front line staff, such as those who work on food distributions, in refugee camps and other vulnerable communities, are still able to move around and carry out their lifesaving activities.
The world is waking up the critical roles that those far from the C-suite are playing to keep this pandemic at bay, and it’s no different in the humanitarian workforce. Indeed 95% of CARE’s workforce come from the countries where we work, and frequently do the work of “essential workers” as now defined in Europe and the USA, but in these vulnerable contexts.
Our ability to control COVID-19 the world over is reliant on our ability to support our weakest nations. For that, we need our humanitarians, and humanitarian supplies, on the ground. And fast.