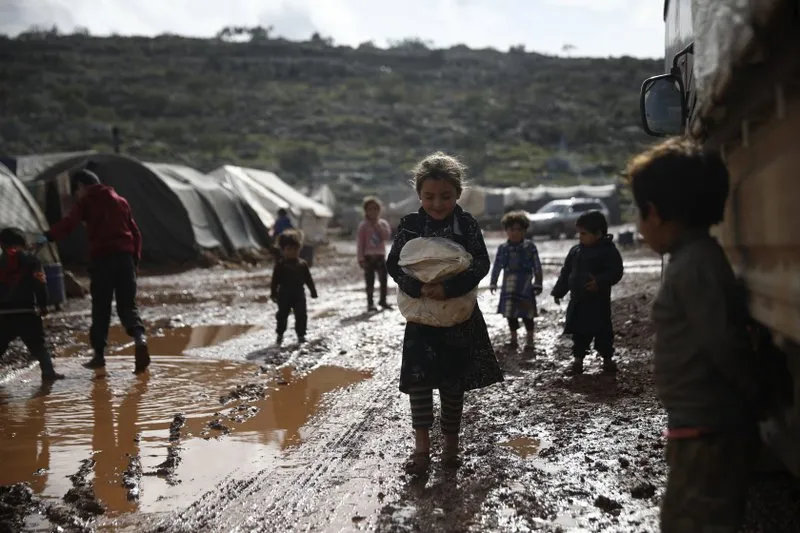
BEIRUT (AP) — At age 19, Fatima al-Omar is at her wits’ end. In the last year alone, she lost her home to fighting in Syria’s last rebel-held enclave and her mother was diagnosed with cancer. She became the sole breadwinner for her mother, three siblings and grandmother as they moved around between shelters.
Then the coronavirus struck, aggravating conditions in northwest Syria just as new fighting had uprooted 1 million people — the biggest wave of displacement in the country’s 10-year war. By late 2020, al-Omar contracted COVID-19, costing her the last job she had picking olives. She hasn’t been able to find work since and is now at risk of another eviction.
Despite the worsening humanitarian situation across war-ravaged Syria, it’s been getting tougher every year to raise money from global donors to help people like al-Omar. The aid community is bracing for significant shortfalls ahead of a donor conference that starts Monday in Brussels and is being co-hosted by the United Nations and the European Union.
CARE International spoke to AP about the lack of funding for Syria.