As we continue to encounter millions around the world who are either vaccine hesitant or in places where vaccines are not yet available, CARE has worked to understand the ways social media can serve as a social and behavior change communication tool to improve public health. Through a groundbreaking partnership with Meta, CARE tested boosted posts to understand what kinds of messaging works best to increase COVID prevention behaviors and vaccine acceptance.
Throughout 2021, CARE launched 45 locally-led campaigns in 20 countries applying lessons learned during an eight-week training series with Meta. In the second half of 2021, participating countries built on their learnings from their first campaigns and attempted to answer new questions that arose all while creating culturally appropriate messaging to encourage the adoption of preventative behaviors and/or to build trust in the vaccine, even if it wasn’t yet available. Although campaign creative was locally developed to respond to unique challenges in each country, CARE wondered if there were universal lessons learned that could be applied globally as social media evolves as a potential tool to drive social and behavioral change.
The TL;DR Summary?
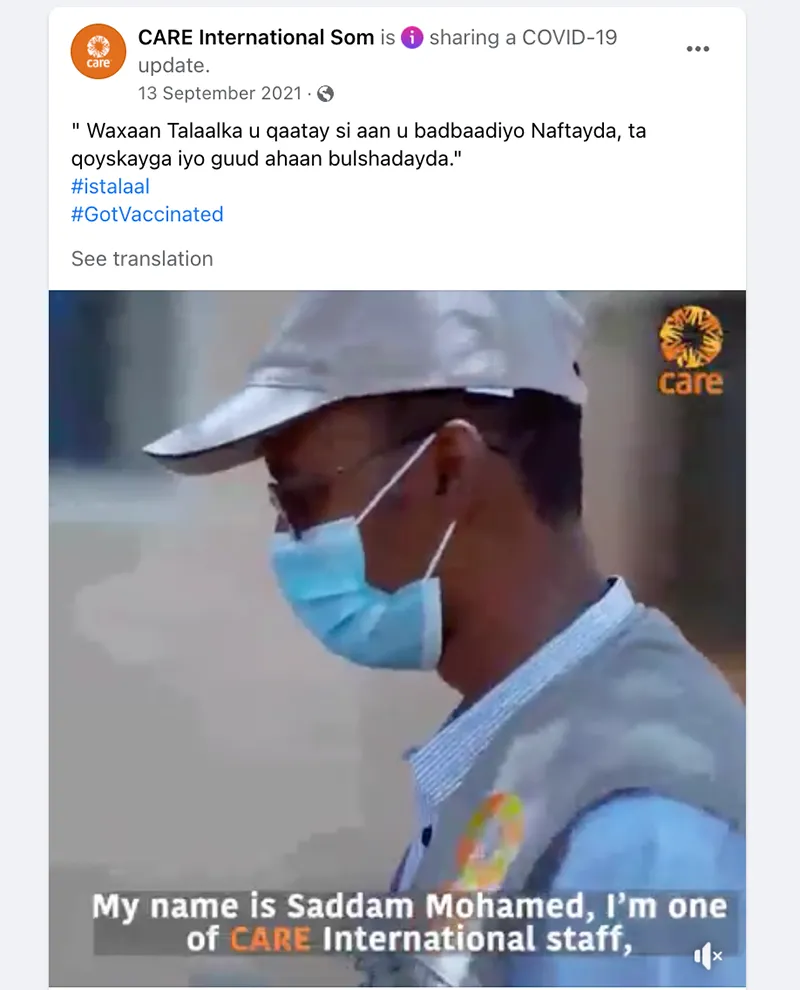
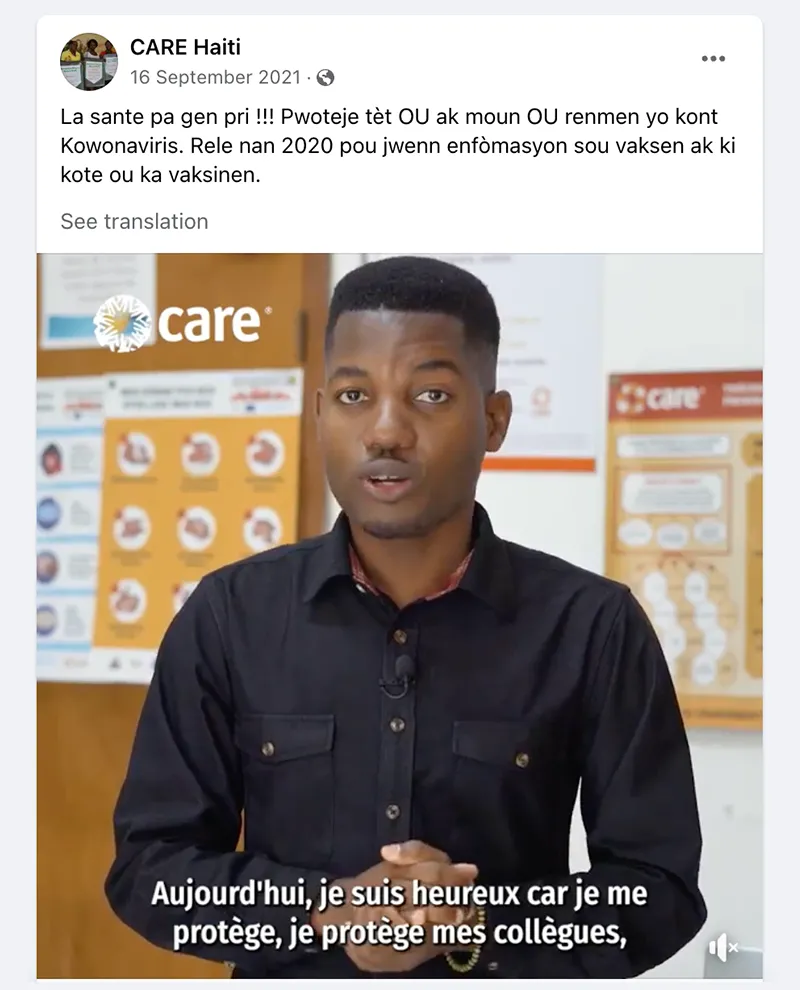
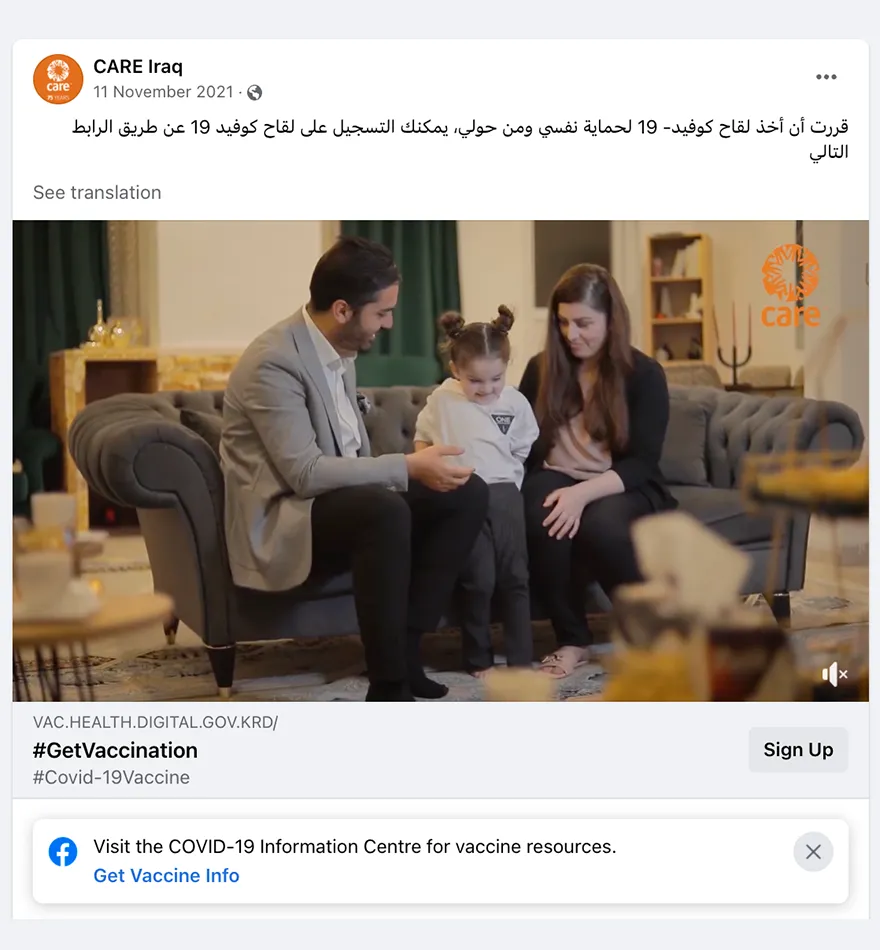
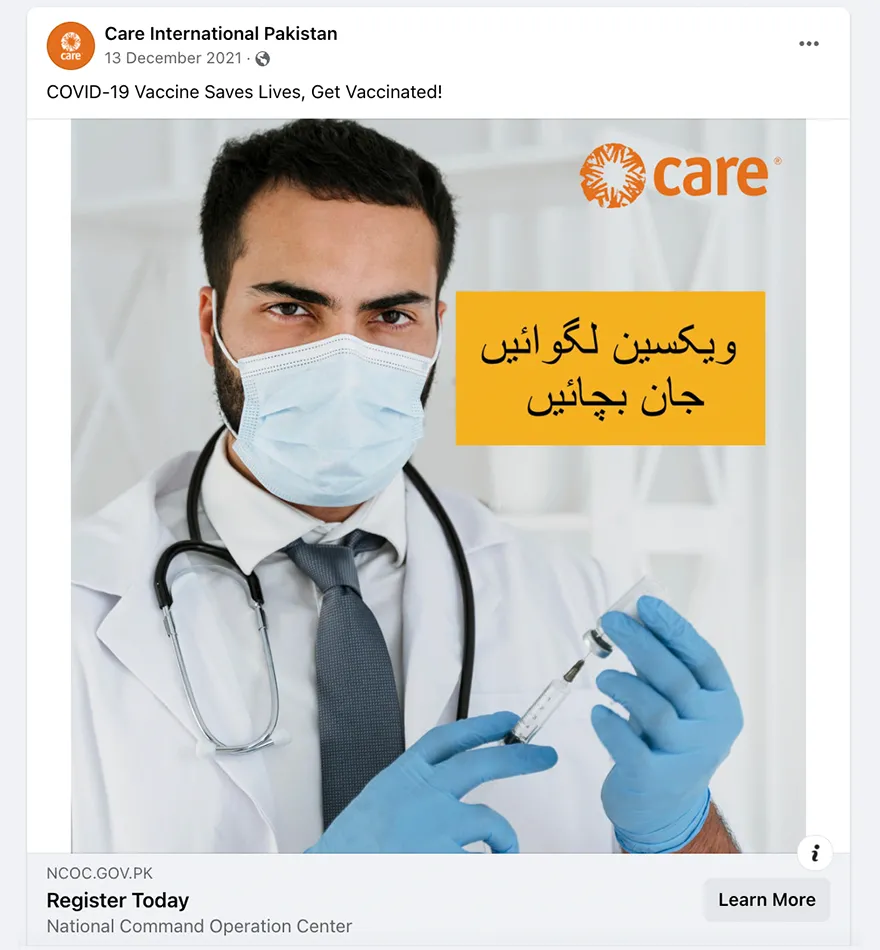
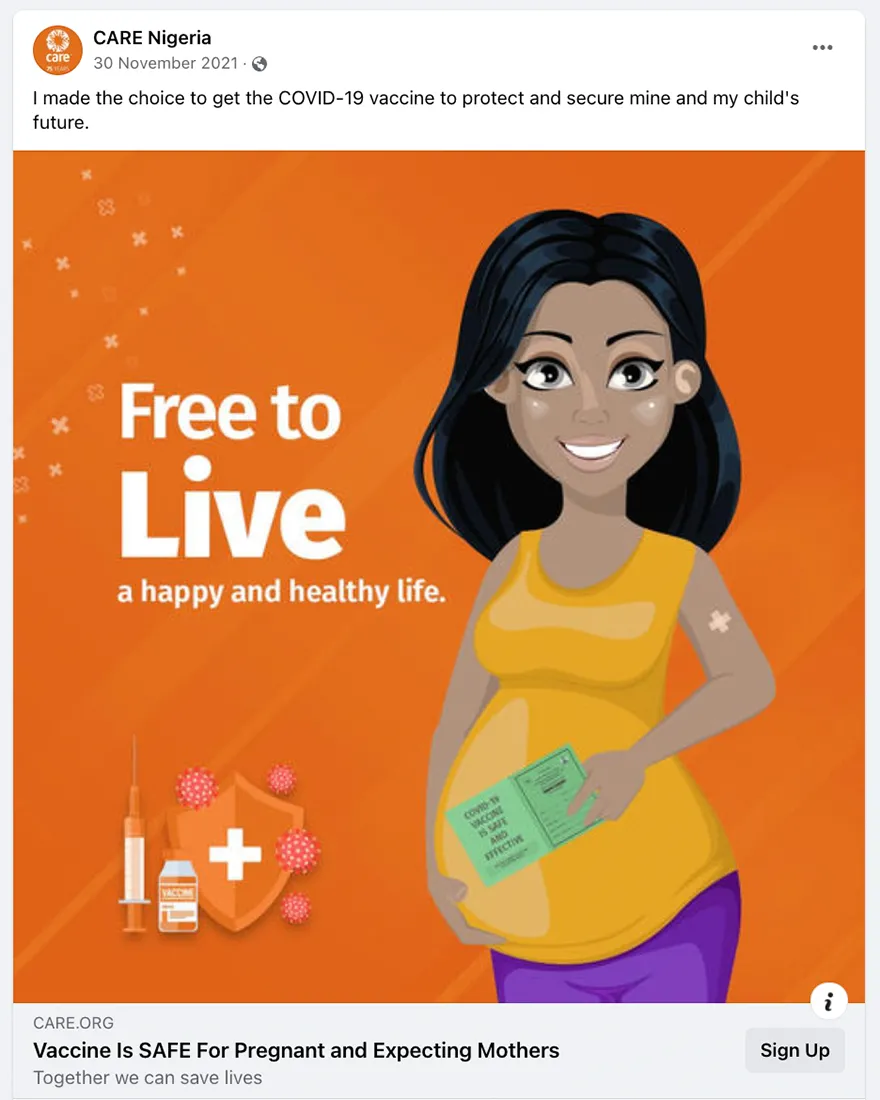
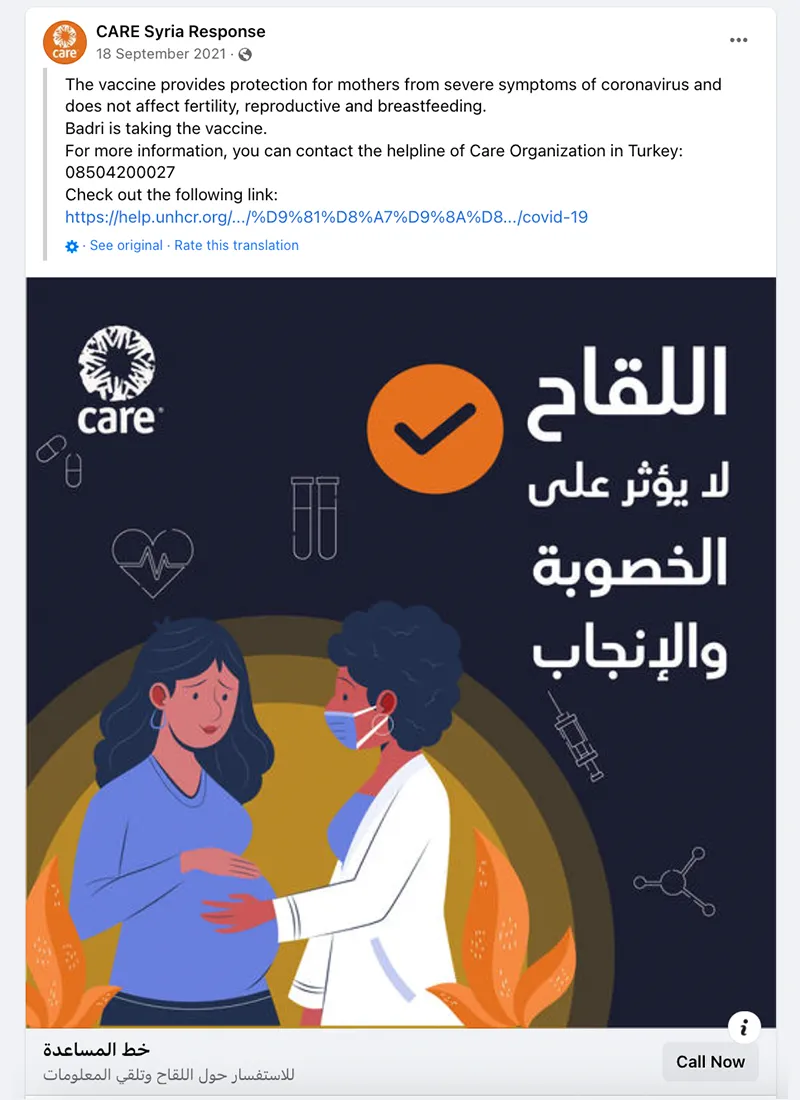
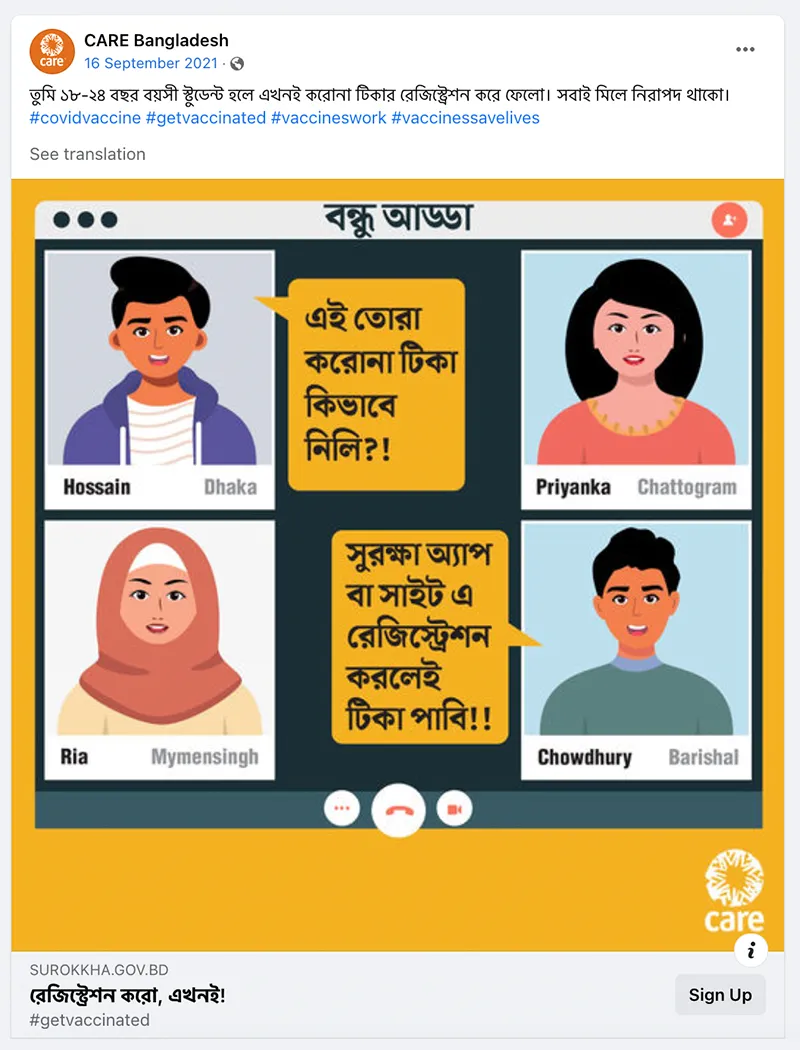
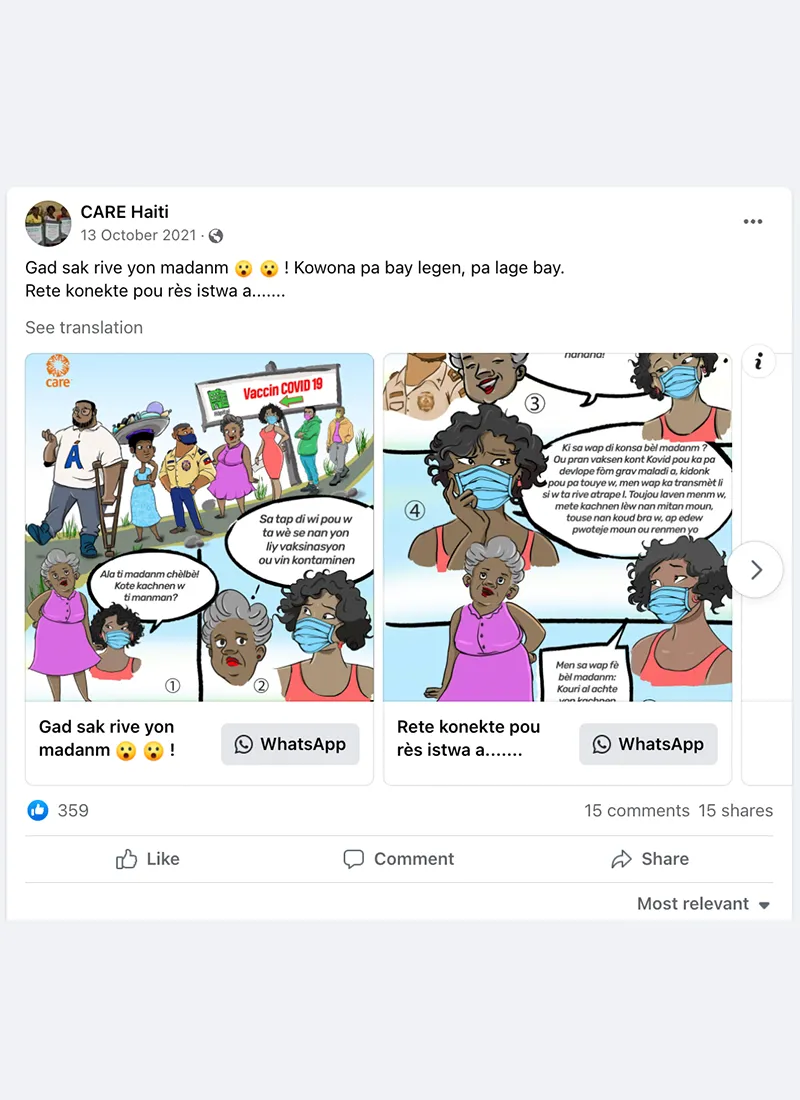
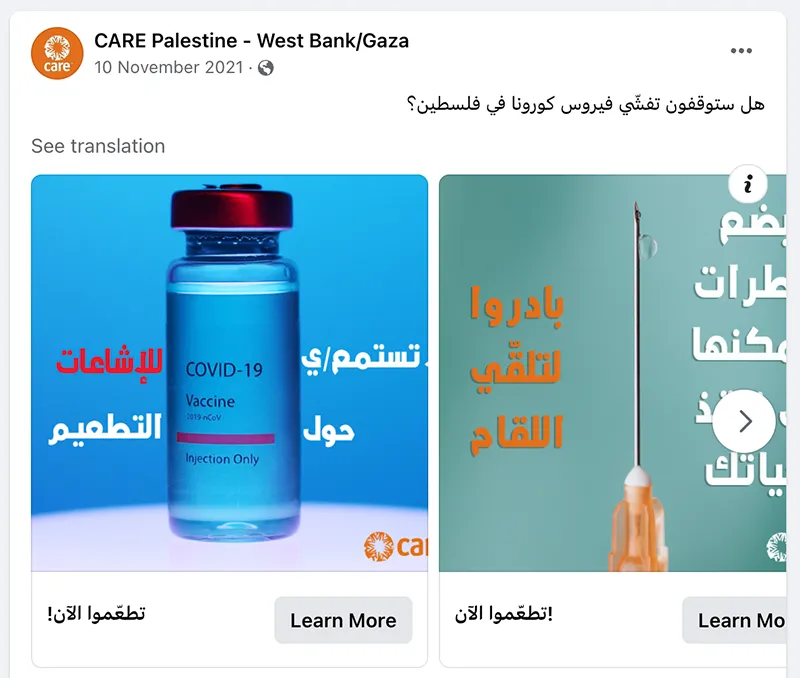
- Trusted messengers are one of the biggest drivers of post engagement. While trusted messengers such as doctors, celebrities, and faith leaders proved powerful, “regular people” like CARE Staff sharing authentic experiences were just, if not more, influential. This was true across all seven countries that tested trusted messengers – Bangladesh, Burundi, Haiti, Iraq, Mali, Somalia, and USA. Similarly, in all CARE campaigns that tested Real People vs. Cartoon imagery, real people not only had stronger communication performance indicators (Iraq, Nigeria, Pakistan), they also drove higher brand lift when we were able to do a multicell test (Bangladesh, Nigeria, USA). This made sense but was also surprising as many campaigns that ran earlier in the year used cartoon images and had strong results.
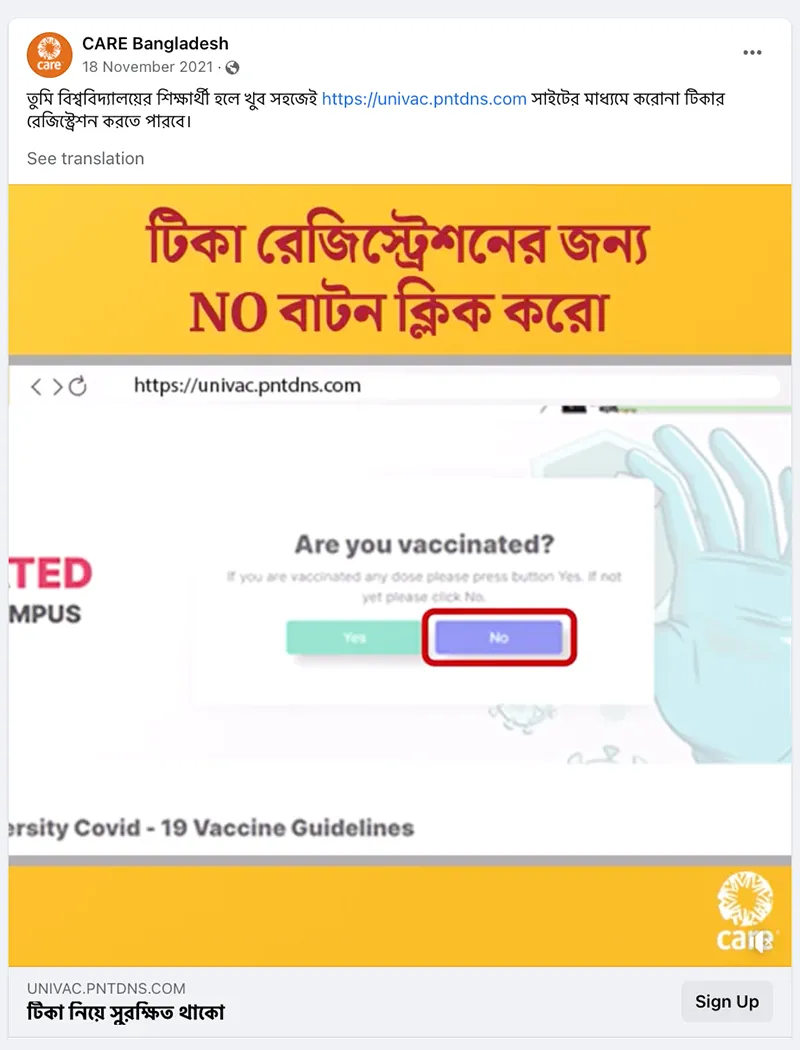
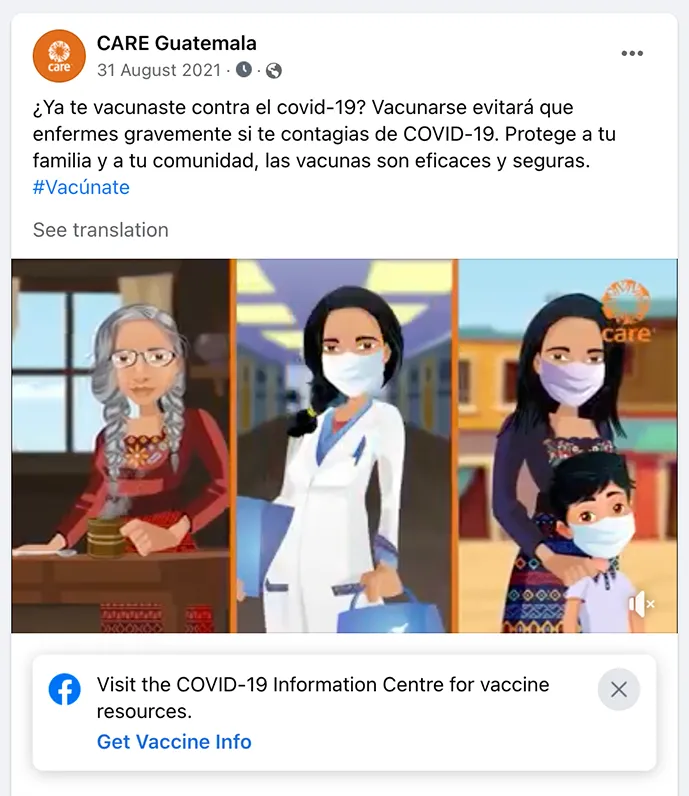
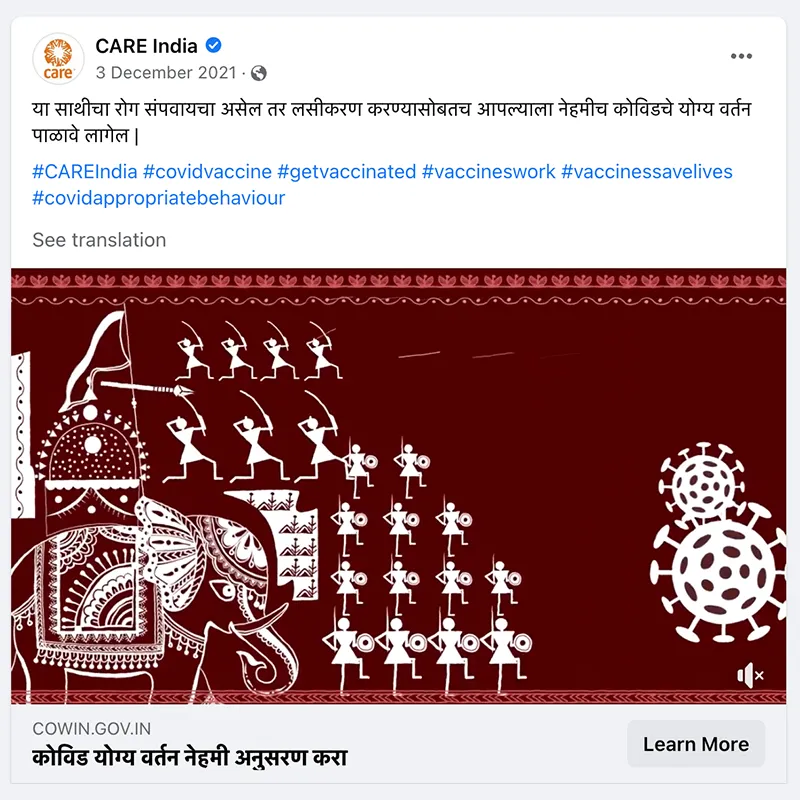
- Personalization is key. Campaigns that personalized content by demographic (CARE Bangladesh), language (CARE Guatemala), and connected it to culture (CARE India) saw communication metrics that were double and triple CARE’s benchmarks.
- Context, context, context. A nuanced understanding of current events, the latest COVID news and policies and cultural distinctions were key. Campaigns that were able to triangulate all three typically had standout communication metrics. Campaigns that did not align underperformed.